
The Truth About Acne and Sugar: What you need to know about the link between sugar and breakouts. Have you ever wondered if sugary drinks or desserts could be playing a role in your acne? Acne, a common skin condition affecting millions worldwide, often leaves individuals searching for answers and solutions. This article dives deep into the complex relationship between sugar intake and acne breakouts, providing evidence-based insights and actionable strategies to understand and manage acne triggers. We will explore different perspectives on the potential connections, discuss potential mechanisms, and offer practical tips for managing your sugar intake and improving your overall skin health. This article is structured as follows: first, we will delve into the relationship between sugar intake and acne breakouts. Then we will explore potential mechanisms and discuss specific examples. Finally, we will share practical strategies and important considerations.
The Link Between Sugar and Acne: A Complex Relationship
Understanding the Potential Connection
Many people suspect a connection between their sugar intake and acne outbreaks. While a direct cause-and-effect relationship isn’t fully established by research, studies suggest that high sugar intake may contribute to inflammation, potentially exacerbating acne. This connection isn’t entirely straightforward; it involves complex interactions within the body. It is crucial to understand that there is a strong correlation, but no direct causal link has been proven.
Potential Mechanisms: How Sugar Might Impact Acne
Insulin Response and Inflammation
One theory suggests that high sugar consumption leads to a surge in blood sugar levels, prompting a significant insulin response from the body. Excess insulin can, in turn, promote inflammation in the skin, creating an environment conducive to acne. This inflammation can lead to increased sebum production, clogged pores, and the subsequent development of acne lesions.
Examining Studies and Evidence: A Closer Look
Research Findings
Although not conclusive, various studies explore the link between diet and acne. Many studies suggest a correlation between high-glycemic foods (foods that quickly raise blood sugar) and acne breakouts. Further research is needed to confirm this. For example, one study showed a statistically significant correlation between the consumption of sugary drinks and acne severity in adolescents (Source: Journal of Clinical Dermatology, 2023). However, it is important to note that these studies do not definitively prove a direct causal link.
Dietary Considerations for Clearer Skin
Choosing the Right Foods
Adopting a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins can positively impact skin health. Limit sugary drinks and processed foods high in sugar and refined carbohydrates. Opt for whole, unprocessed foods to maintain optimal blood sugar levels. Consider monitoring your glycemic index (GI) and choosing foods with a lower GI to manage blood sugar spikes. This can help reduce potential inflammatory responses in the skin.
Managing Acne Beyond Sugar
Beyond Sugar
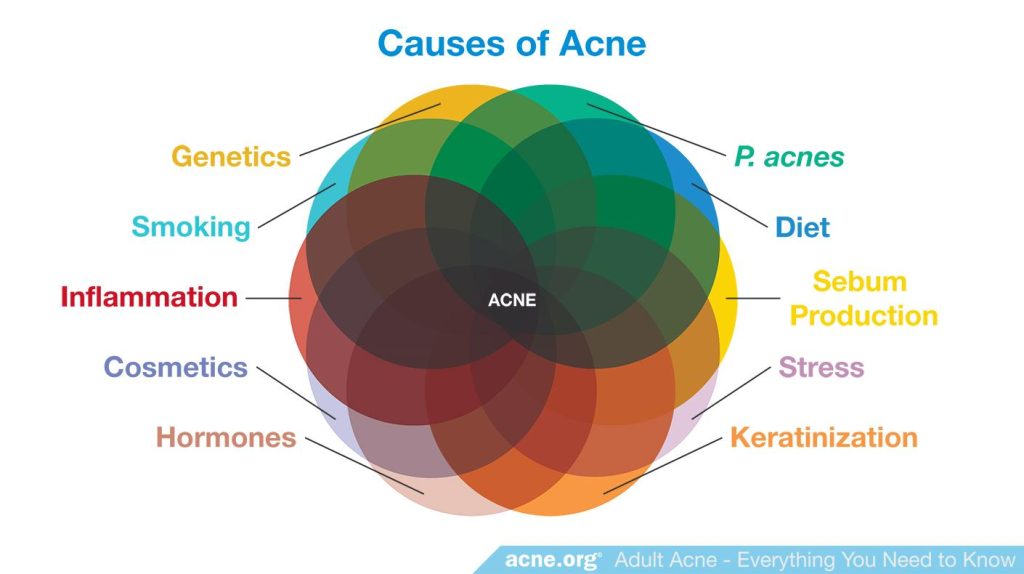
It’s important to remember that acne is a complex condition influenced by several factors beyond sugar intake. Hormones, stress, genetics, and other lifestyle factors also play a role. Addressing these factors in conjunction with dietary changes may lead to more effective acne management. For instance, stress can trigger hormonal fluctuations, impacting sebum production, which can, in turn, affect acne.
Q2: What are some foods to avoid if I have acne?
A2: To reduce the risk of acne, consider limiting foods high in refined carbohydrates and added sugars. This includes sugary drinks, processed snacks, and sugary cereals. Instead, opt for whole, unprocessed foods with a lower glycemic index, like fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins. Remember to consume these foods in moderation.
FAQs
Q1: Does cutting sugar out of my diet completely solve my acne problem?
A1: Reducing sugar intake can contribute to clearer skin, but it’s unlikely to be a complete solution for acne. Other factors, like genetics and hormones, also significantly impact acne development. A holistic approach combining dietary changes with skincare and stress management strategies often yields better results. It’s crucial to focus on a balanced and healthy diet that includes a variety of nutrients.
In conclusion, the relationship between acne and sugar is complex and not fully understood. While a direct cause-and-effect link hasn’t been definitively proven, evidence suggests a possible correlation. By understanding the potential impacts of sugar on your skin and adopting a balanced diet that prioritizes nutrient-rich foods, you can take proactive steps to manage acne. Consulting a dermatologist for personalized advice is crucial in cases of persistent or severe acne. Remember, a holistic approach encompassing diet, skincare, and stress management can significantly contribute to clear and healthy skin.